mirror of
https://github.com/lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-docker-sdk.git
synced 2026-02-08 04:30:04 +03:00
Compare commits
8 Commits
v0.0.2
...
fix_multip
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
6417e81cd0 | ||
|
|
44f236e9cd | ||
|
|
002d69b364 | ||
|
|
be7e625e2b | ||
|
|
f6fd10e14b | ||
|
|
8c283d7619 | ||
|
|
0a2bba1365 | ||
|
|
b7da9deed4 |
77
.github/workflows/sdk-ci.yml
vendored
77
.github/workflows/sdk-ci.yml
vendored
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||
name: Raspberry PI Pico Docker SDK CI
|
||||
|
||||
name: Build, test and push Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
@@ -14,34 +15,64 @@ env:
|
||||
TEST_TAG: pico_test_sdk
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
sdk_container:
|
||||
build-and-test:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Build SDK
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
load: true
|
||||
tags: ${{ env.TEST_TAG }}
|
||||
- name: Test SDK
|
||||
run: bash ./test_sdk.sh ${{ env.TEST_TAG }}
|
||||
- name: Log into Docker Hub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up QEMU (for ARM builds)
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-qemu-action@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ github.actor }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Extract SDK metadata
|
||||
id: meta
|
||||
uses: docker/metadata-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
images: lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk
|
||||
- name: Push SDK image
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'release' && github.event.action == 'published'
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build Docker image (multi-arch, no push)
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
id: build
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
platforms: linux/amd64
|
||||
push: false
|
||||
load: true # Allows testing the image locally
|
||||
tags: ${{ env.TEST_TAG }}
|
||||
cache-from: type=gha
|
||||
cache-to: type=gha,mode=max
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run Tests (from built image)
|
||||
run: bash ./test_sdk.sh ${{ env.TEST_TAG }}
|
||||
|
||||
push-image:
|
||||
needs: build-and-test
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up QEMU
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-qemu-action@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ github.actor }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and Push Docker image (multi-arch)
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
platforms: linux/amd64,linux/arm64
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
|
||||
labels: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.labels }}
|
||||
tags: lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk:latest
|
||||
cache-from: type=gha
|
||||
cache-to: type=gha,mode=max
|
||||
|
||||
49
Dockerfile
49
Dockerfile
@@ -1,21 +1,29 @@
|
||||
FROM alpine:3.17.0
|
||||
FROM ubuntu:24.10 AS gcc_build
|
||||
|
||||
# Install toolchain
|
||||
RUN apk update && \
|
||||
apk upgrade && \
|
||||
apk add git \
|
||||
python3 \
|
||||
py3-pip \
|
||||
cmake \
|
||||
build-base \
|
||||
libusb-dev \
|
||||
bsd-compat-headers \
|
||||
newlib-arm-none-eabi \
|
||||
gcc-arm-none-eabi
|
||||
# Build GCC RISC-V
|
||||
COPY ./install_gcc.sh /home/install_gcc.sh
|
||||
RUN bash /home/install_gcc.sh
|
||||
|
||||
FROM ubuntu:24.10 AS sdk_setup
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get update -y && \
|
||||
apt-get upgrade -y && \
|
||||
apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
python3 \
|
||||
tar \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
gcc-arm-none-eabi \
|
||||
libnewlib-arm-none-eabi \
|
||||
libstdc++-arm-none-eabi-newlib \
|
||||
cmake && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
|
||||
# Raspberry Pi Pico SDK
|
||||
ARG SDK_PATH=/usr/local/picosdk
|
||||
RUN git clone --depth 1 --branch 1.5.1 https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk $SDK_PATH && \
|
||||
RUN git clone --depth 1 --branch 2.1.1 https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk $SDK_PATH && \
|
||||
cd $SDK_PATH && \
|
||||
git submodule update --init
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,18 +31,23 @@ ENV PICO_SDK_PATH=$SDK_PATH
|
||||
|
||||
# FreeRTOS
|
||||
ARG FREERTOS_PATH=/usr/local/freertos
|
||||
RUN git clone --depth 1 --branch V11.0.1 https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel $FREERTOS_PATH && \
|
||||
RUN git clone --depth 1 --branch V11.2.0 https://github.com/FreeRTOS/FreeRTOS-Kernel $FREERTOS_PATH && \
|
||||
cd $FREERTOS_PATH && \
|
||||
git submodule update --init --recursive
|
||||
|
||||
ENV FREERTOS_KERNEL_PATH=$FREERTOS_PATH
|
||||
|
||||
# Picotool installation
|
||||
RUN git clone --depth 1 --branch 1.1.2 https://github.com/raspberrypi/picotool.git /home/picotool && \
|
||||
RUN git clone --depth 1 --branch 2.1.1 https://github.com/raspberrypi/picotool.git /home/picotool && \
|
||||
cd /home/picotool && \
|
||||
mkdir build && \
|
||||
cd build && \
|
||||
cmake .. && \
|
||||
make && \
|
||||
cp /home/picotool/build/picotool /bin/picotool && \
|
||||
make -j$(nproc) && \
|
||||
cmake --install . && \
|
||||
rm -rf /home/picotool
|
||||
|
||||
# Install GCC RISC-V
|
||||
COPY --from=gcc_build /opt/riscv/gcc14-rp2350-no-zcmp /opt/riscv/gcc14-rp2350-no-zcmp
|
||||
ENV PATH="$PATH:/opt/riscv/gcc14-rp2350-no-zcmp/bin"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
187
README.md
187
README.md
@@ -2,140 +2,155 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Raspberry Pi Pico Docker SDK
|
||||
|
||||
Lightweight Raspberry Pi Pico C++ SDK container.
|
||||
A SDK environment for Raspberry Pi Pico 1 and 2 in a Docker container.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pull container from Docker Hub and run
|
||||
## Pulling the Image from Docker Hub and Running
|
||||
|
||||
The latest version of the image is stored on [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk/general)
|
||||
and can be used for container runs.
|
||||
Commands below show how to run a container, using an image from Docker Hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
The latest image is available on [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk/general)
|
||||
and can be used to run a container.
|
||||
The following commands show how to run the container using the Docker Hub image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk:latest
|
||||
|
||||
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The directory from which the `docker run` command was called will be mounted to /home/dev in the container.
|
||||
So after attaching to the SDK container you can build your project following the steps:
|
||||
The directory from which the `docker run` command was executed will be mounted in the container at `/home/dev`.
|
||||
After attaching to the SDK container, you can build your project by executing the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /home/dev
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
|
||||
cmake .. && make -j4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Build image and run container:
|
||||
## Building the Image and Running the Container
|
||||
|
||||
To build your own SDK image, You need to clone this repository and run the following commands:
|
||||
To build your own SDK image, clone this repository and run the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd raspberry-pi-pico-docker-sdk
|
||||
|
||||
docker build . --tag pico-sdk
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev pico-sdk
|
||||
|
||||
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Visual Studio Code as Rassberry Pi PICO projects IDE
|
||||
## Visual Studio Code as IDE for Raspberry Pi Pico Projects
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the SDK container with Visual Studio Code as Raspberry Pi Pico projects IDE.
|
||||
You can use the SDK container with Visual Studio Code to create an IDE for Raspberry Pi Pico projects.
|
||||
There are two solutions prepared: a new one using the Visual Studio Dev Containers extension and an old one with manual configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
### Attaching VSCode to SDK Docker container
|
||||
### [Visual Studio Code Dev Container](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/devcontainers/containers)
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instruction below to set up VSCode:
|
||||
#### Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
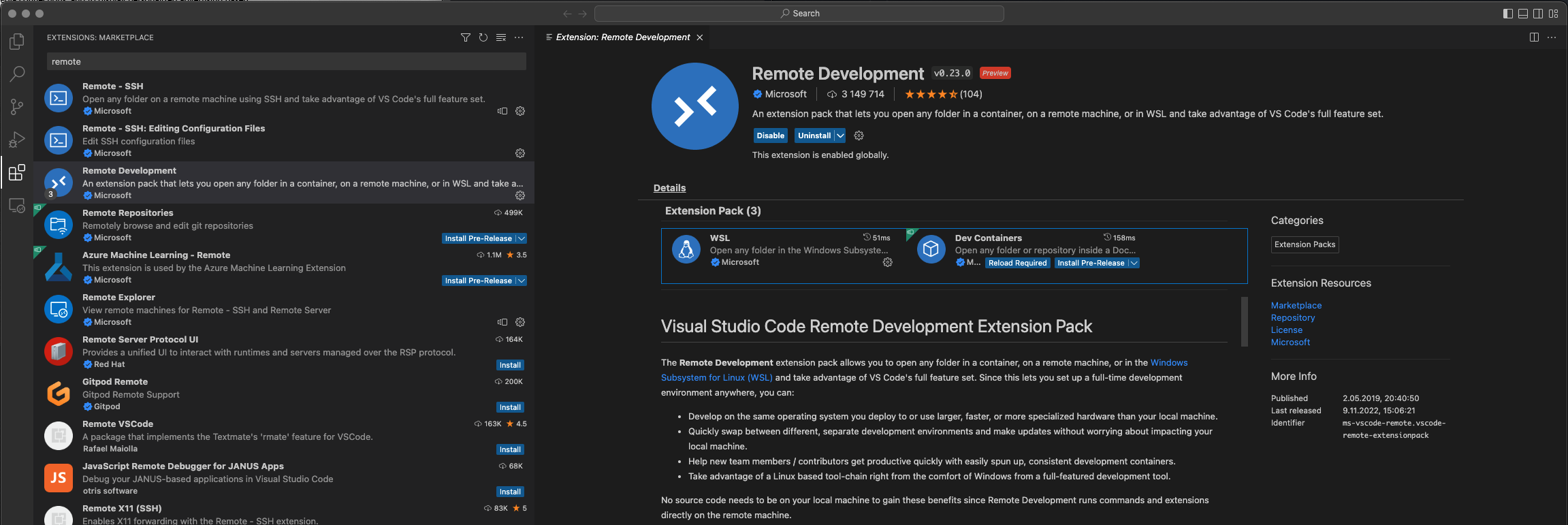
1. Install [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) and next [Remote Development](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode-remote.vscode-remote-extensionpack) extensions.
|
||||
To use the dev container, you need to have VSCode, Docker, and the VSCode extensions installed.
|
||||
Follow [this](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/devcontainers/tutorial#_prerequisites) guide for setup.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using the Dev Container for Pico IDE
|
||||
|
||||
2. Open the terminal and go to the projects you want to open in VSCode.
|
||||
- Clone [pico-template-project](https://github.com/lukstep/pico-template-project) repository.
|
||||
- Open `pico-template-project` folder in Visual Studio Code.
|
||||
- In VSCode, click the button in the bottom left corner of VSCode and select: Reopen in Container...
|
||||

|
||||
- Build the project.
|
||||
- Enjoy coding you Pico project with Intellisense.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. Pull SDK image from Docker HUB and run SDK container via the following command. The container must be running while you attach to it via VSCode.
|
||||
## Pico Memory Flashing and Debugging via Pico Probe and OpenOCD
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk:latest
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> OpenOCD not support RP2350 (Pico 2). Currently this part is only valid for RP2040 boards (Pico 1).
|
||||
|
||||
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
||||
To work efficiently on the project, we need the ability to upload firmware to the microcontroller, debug, and communicate through the serial port. The Raspberry Pi Pico board itself allows for software uploads, but this process is not very convenient or efficient for larger projects. The Pico Probe extends the capabilities of the Raspberry Pi Pico board to include fast firmware uploads to the microcontroller's memory, debugging via Serial Wire Debug (SWD), and it also serves as a USB UART converter.
|
||||
|
||||
The Debug Probe is compatible with the CMSIS-DAP interface, allowing OpenOCD to be used as the debugger server. By using OpenOCD, it becomes possible to communicate between development containers and the Debug Probe via TCP. On Linux, the Docker container can communicate directly through COM ports. However, on Mac and Windows, this is not possible because Docker runs in a dedicated virtual machine that does not have access to COM ports. Therefore, a solution with the OpenOCD server on the host machine was chosen.
|
||||
|
||||
The diagram below shows the environment topology:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Pico Probe is connected to the Raspberry Pi Pico board:
|
||||
|
||||
- SWD (Serial Wire Debug) interface for debugging.
|
||||
- UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) interface for serial communication.
|
||||
|
||||
2. The Pico Probe is connected to the PC via USB.
|
||||
|
||||
3. OpenOCD (Open On-Chip Debugger) runs on the PC and communicates with the Pico Probe.
|
||||
|
||||
4. The development container (devContainer) connects to OpenOCD via TCP.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Instal required tools
|
||||
|
||||
To install OpenOCD on Linux, run the following command in a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo apt install openocd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
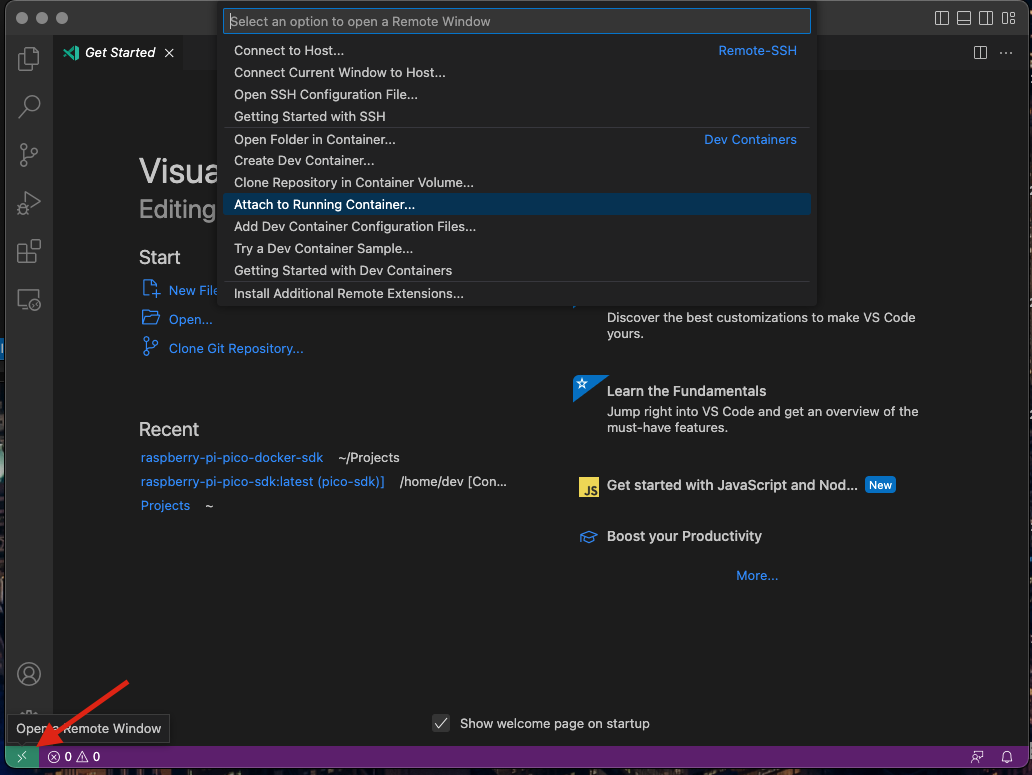
4. When the container is launched, go to VSCode, click the green button in the lower left corner of VSCode and select options: Attach to Running Container...
|
||||
To install OpenOCD on macOS, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
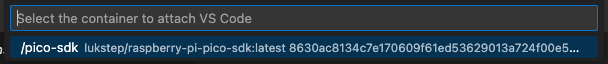
5. Select the SDK container.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
6. Then a new VSCode window will open. At the bottom window, you can see that it is attached to the SDK container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
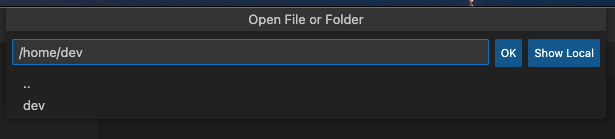
7. Now, there is needed to open project files. Your project is mounted to `/home/dev` in the container. Go to EXPLORE tab in VSCode and click Open Folder. In opened window write `/home/dev` and click the OK button.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
8. Now You can explore, develop and build your Raspberry Pi Pico project via Visual Studio Code!
|
||||
|
||||
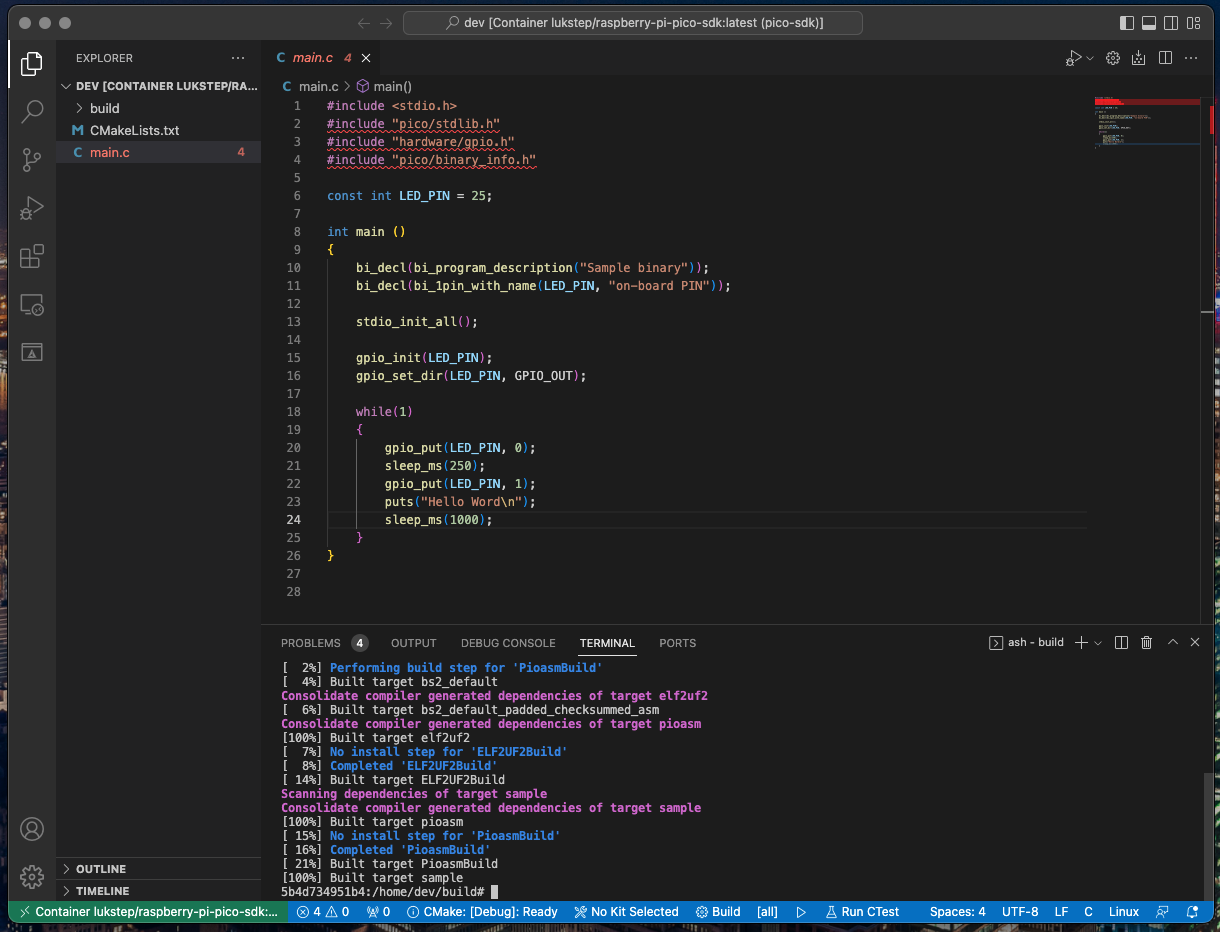
|
||||
|
||||
### Pico SDK aware Intellisense
|
||||
|
||||
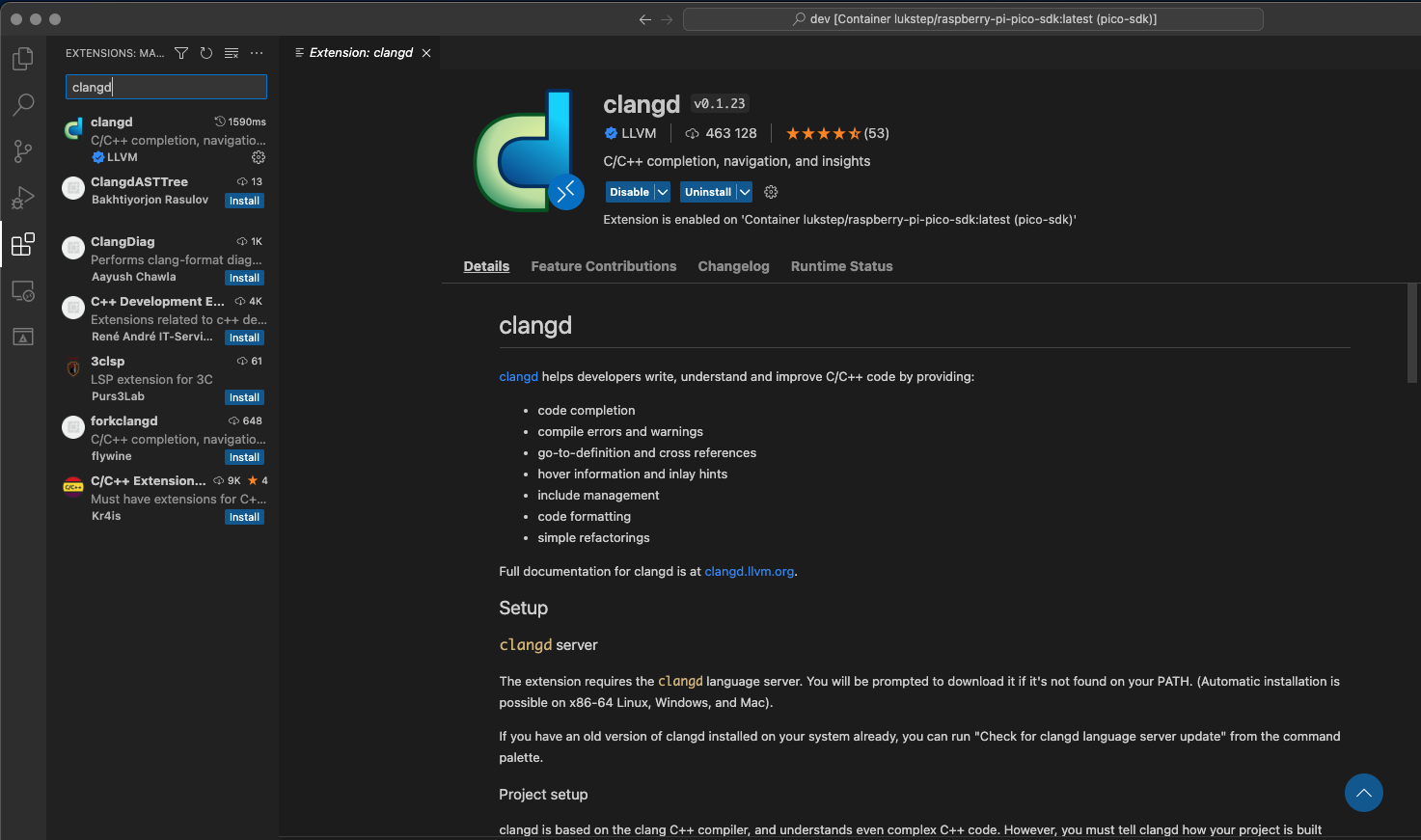
For an IntelliSense that will be aware of Raspberry Pi Pico SDK dependencies, we will use [Clangd](https://clangd.llvm.org). Clangd is a C/C++ language server provided by the LLVM project. To Setup Clang as Intellisense engine follow instruction below:
|
||||
|
||||
1. To begin with, you need to install the server itself (Clangd is not installed by default in the SDK container image), to do this in the terminal call the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
apk add clang-extra-tools
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
brew install openocd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Next is needed to install the Visual Studio Code [Clangd extension](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=llvm-vs-code-extensions.vscode-clangd).
|
||||
To install OpenOCD on Windows, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Go to the page https://github.com/xpack-dev-tools/openocd-xpack/releases.
|
||||
|
||||
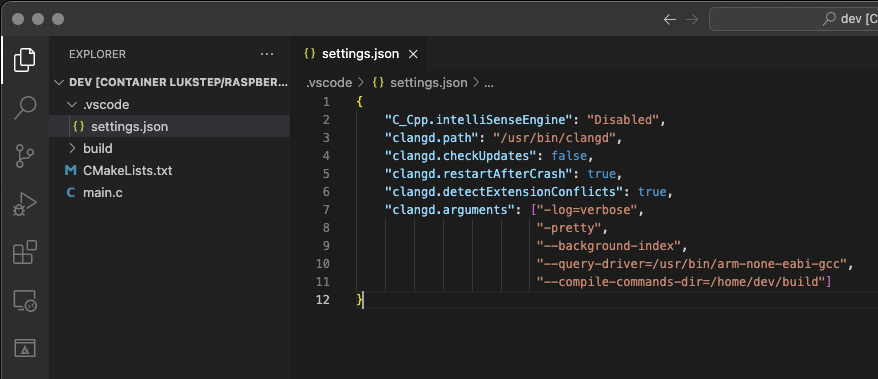
1. To set-up The Clangd extension, in the project root directory, create folder .vcode with file settings.json. To settings.json past configuration from the snippet below:
|
||||
- Download the Windows build of OpenOCD. For example, you might download a file named xpack-openocd-0.12.0-2-win32-x64.zip.
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"C_Cpp.intelliSenseEngine": "Disabled",
|
||||
"clangd.path": "/usr/bin/clangd",
|
||||
"clangd.checkUpdates": false,
|
||||
"clangd.restartAfterCrash": true,
|
||||
"clangd.detectExtensionConflicts": true,
|
||||
"clangd.arguments": ["-log=verbose",
|
||||
"-pretty",
|
||||
"--background-index",
|
||||
"--query-driver=/usr/bin/arm-none-eabi-gcc",
|
||||
"--compile-commands-dir=/home/dev/build"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Unzip the downloaded file to extract its contents.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use: Step-by-Step Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
1. Connect the Pico Probe to the Pico Board via SWD (1) and connect the Pico board UART to the UART-USB converter on the Pico Probe (2).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4. For clangd to work, it needs a `compile_commands.json` file. This file contains the compilation and dependency information of each file in the project. To create it you need to add to the CMake command, `-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1`. So You need to build your project with the command:
|
||||
2. Connect the Pico Probe and Pico Board to your PC
|
||||
|
||||
3. Start the OpenOCD
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
On Linux and Mac, open a new terminal and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo openocd -f interface/cmsis-dap.cfg -f target/rp2040.cfg -c 'bindto 0.0.0.0' -c 'adapter speed 5000' -c 'init'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
cmake -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1 ..
|
||||
On Windows, open PowerShell, navigate to the folder containing OpenOCD, and run `openocd.exe`:
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd .\Desktop\xpack-openocd-0.12.0-2\
|
||||
.\bin\openocd.exe -f interface\cmsis-dap.cfg -f target\rp2040.cfg -c 'bindto 0.0.0.0' -c 'adapter speed 5000' -c 'init'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Now IntelliSense should work!. Now you should see a prompt when you start typing. If you hover your cursor over a function from the SDK you should see its documentation, You can go to the function definition by pressing F12.
|
||||
4. Open the project in the Dev Container.
|
||||
|
||||
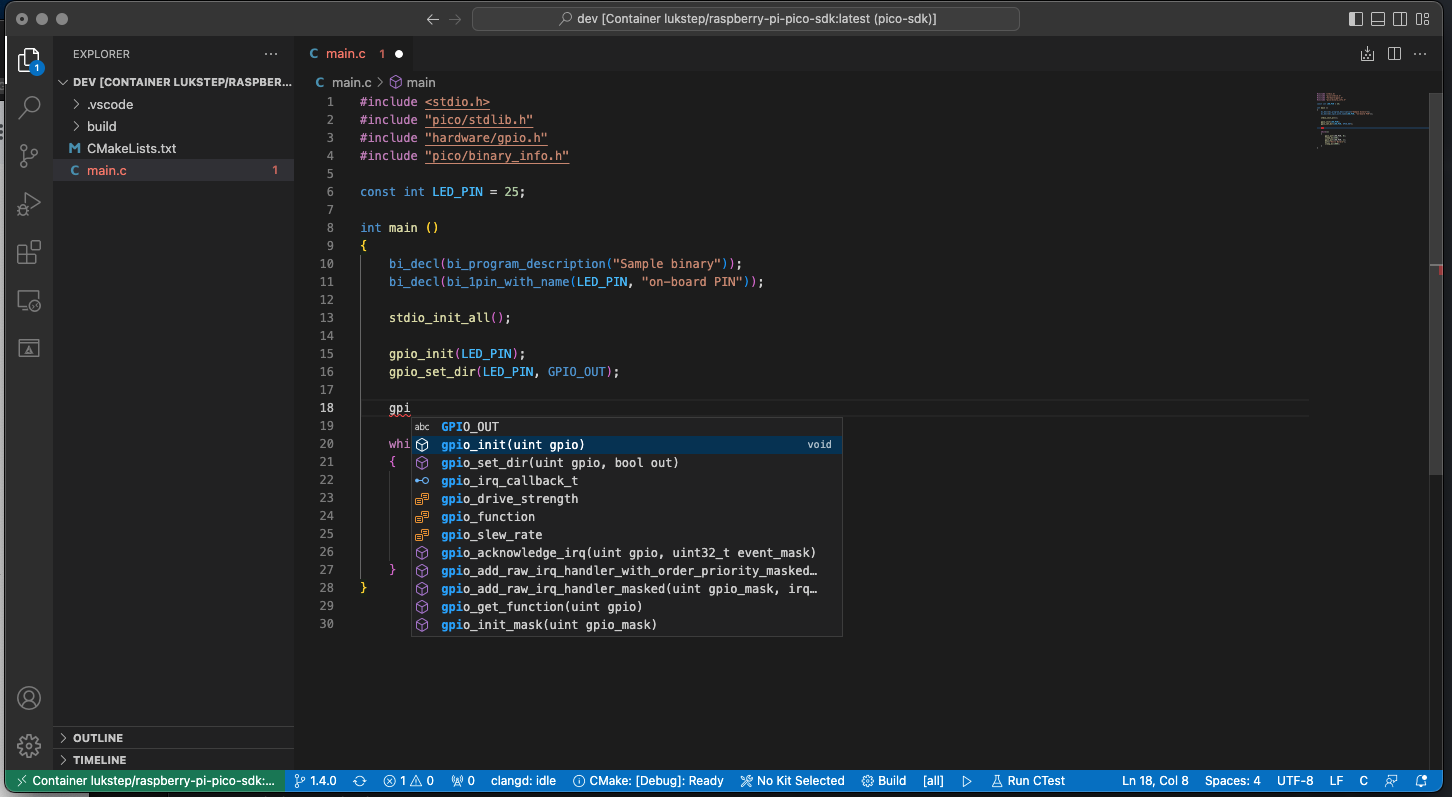
|
||||
5. Make a debug build. Go to the CMake extension tab (1), click "Select Variant" (2), and choose "Debug" build (3). Start the build (4). If the build completes successfully, you can proceed to flashing the memory and debugging.
|
||||
|
||||
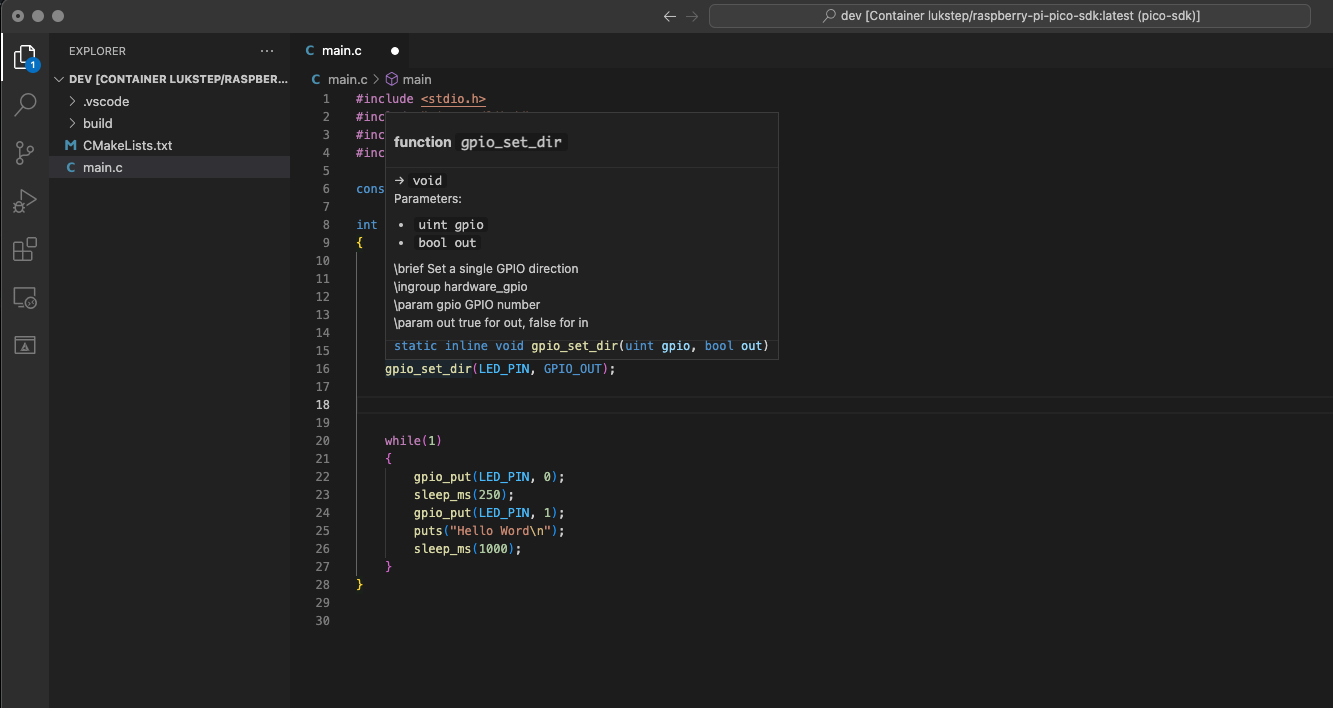
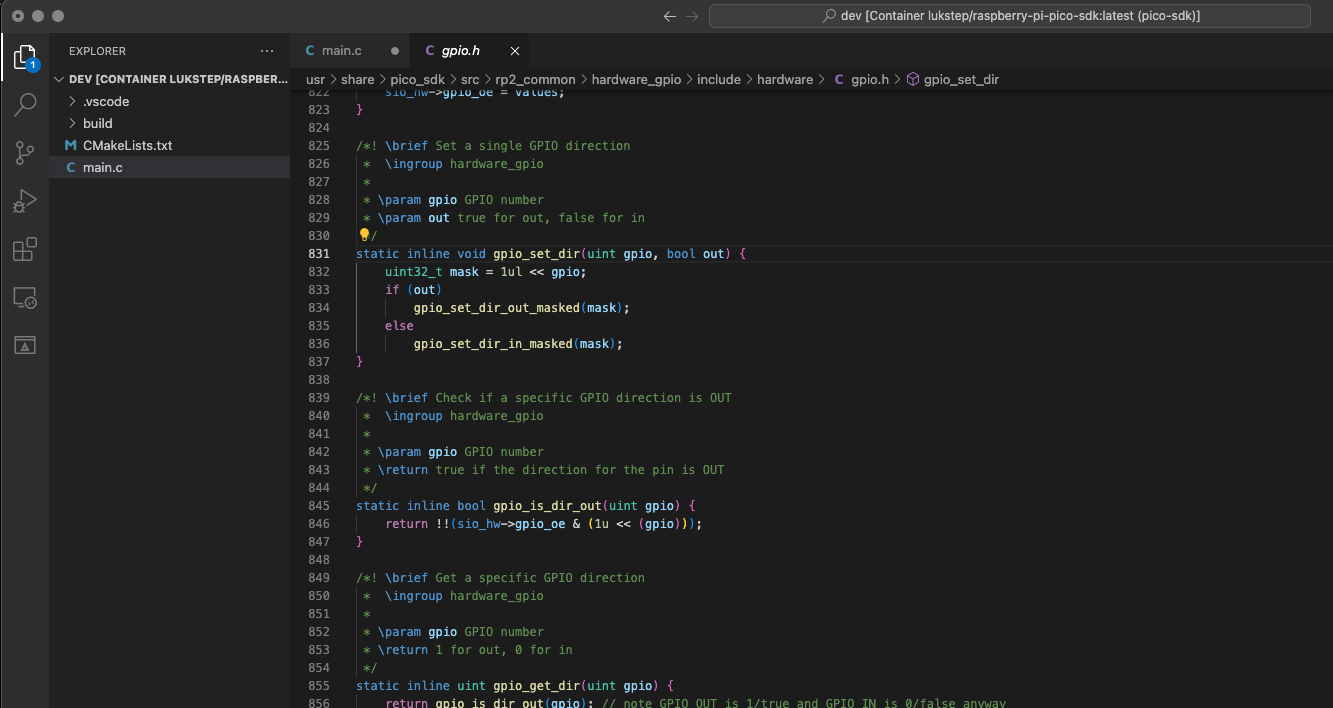
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
6. To start a debug session, first add a breakpoint in the main function. Next, go to the debugger extension tab (1), and click "Play" (2). The debug session starts by flashing the Pico's memory and restarting the microcontroller. After the reset, the flashed firmware starts and the program should stop at the breakpoint.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to flash the Pico's memory without starting a debugger session. To do that, run the preprogrammed tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
- Press Ctrl+Shift+P (Windows/Linux) or Cmd+Shift+P (Mac) to open the Command Palette.
|
||||
- Type Run Task into the Command Palette and press Enter.
|
||||
- Select task `Flash`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Manual configuration of VSCode as Pico IDE (old)
|
||||
|
||||
Refer [here](docs/vscode_manual_setup.md) for step-by-step instruction
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
[Raspberry Pi Debug Probe](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/microcontrollers/debug-probe.html)
|
||||
|
||||
[Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ SDK](https://datasheets.raspberrypi.com/pico/raspberry-pi-pico-c-sdk.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
[OpenOCD project page](https://openocd.org)
|
||||
|
||||
94
docs/vscode_manual_setup.md
Normal file
94
docs/vscode_manual_setup.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Manual configuration of VSCode as Pico IDE
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
You need to Visual Studio Code and Docker installed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Attaching VSCode to SDK Docker container
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instruction below to set up VSCode:
|
||||
|
||||
- Install [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) and next [Remote Development](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode-remote.vscode-remote-extensionpack) extensions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- Open the terminal and go to the projects you want to open in VSCode.
|
||||
|
||||
- Pull SDK image from Docker HUB and run SDK container via the following command. The container must be running while you attach to it via VSCode.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk:latest
|
||||
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- When the container is launched, go to VSCode, click the green button in the lower left corner of VSCode and select options: Attach to Running Container...
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- Select the SDK container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- Then a new VSCode window will open. At the bottom window, you can see that it is attached to the SDK container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- Now, there is needed to open project files. Your project is mounted to `/home/dev` in the container. Go to EXPLORE tab in VSCode and click Open Folder. In opened window write `/home/dev` and click the OK button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- Now You can explore, develop and build your Raspberry Pi Pico project via Visual Studio Code!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Pico SDK aware Intellisense
|
||||
|
||||
For an IntelliSense that will be aware of Raspberry Pi Pico SDK dependencies, we will use [Clangd](https://clangd.llvm.org). Clangd is a C/C++ language server provided by the LLVM project. To Setup Clang as Intellisense engine follow instruction below:
|
||||
|
||||
- To begin with, you need to install the server itself (Clangd is not installed by default in the SDK container image), to do this in the terminal call the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
apk add clang-extra-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Next is needed to install the Visual Studio Code [Clangd extension](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=llvm-vs-code-extensions.vscode-clangd).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- To set-up The Clangd extension, in the project root directory, create folder .vcode with file settings.json. To settings.json past configuration from the snippet below:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"C_Cpp.intelliSenseEngine": "Disabled",
|
||||
"clangd.path": "/usr/bin/clangd",
|
||||
"clangd.checkUpdates": false,
|
||||
"clangd.restartAfterCrash": true,
|
||||
"clangd.detectExtensionConflicts": true,
|
||||
"clangd.arguments": ["-log=verbose",
|
||||
"-pretty",
|
||||
"--background-index",
|
||||
"--query-driver=/usr/bin/arm-none-eabi-gcc",
|
||||
"--compile-commands-dir=/home/dev/build"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- For clangd to work, it needs a `compile_commands.json` file. This file contains the compilation and dependency information of each file in the project. To create it you need to add to the CMake command, `-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1`. So You need to build your project with the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
cmake -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1 ..
|
||||
make
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Now IntelliSense should work!. Now you should see a prompt when you start typing. If you hover your cursor over a function from the SDK you should see its documentation, You can go to the function definition by pressing F12.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
51
install_gcc.sh
Normal file
51
install_gcc.sh
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
RET_VALUE=$?
|
||||
RED='\033[0;31m'
|
||||
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get update -y && \
|
||||
apt-get upgrade -y && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y autoconf automake autotools-dev curl python3 python3-pip libmpc-dev libmpfr-dev libgmp-dev gawk build-essential bison flex texinfo gperf libtool patchutils bc zlib1g-dev libexpat-dev ninja-build git cmake libglib2.0-dev libslirp-dev
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if [ $RET_VALUE != 0 ]; then
|
||||
echo "${RED}Instalation failed!${NC}"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /opt/riscv/gcc14-rp2350-no-zcmp
|
||||
|
||||
chown -R "$(whoami)" /opt/riscv/gcc14-rp2350-no-zcmp
|
||||
|
||||
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain /home/riscv-gnu-toolchain
|
||||
|
||||
if [ $RET_VALUE != 0 ]; then
|
||||
echo "${RED}Cloning RISC-V repo failed!${NC}"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
cd /home/riscv-gnu-toolchain || exit
|
||||
|
||||
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc gcc-14 -b releases/gcc-14
|
||||
|
||||
if [ $RET_VALUE != 0 ]; then
|
||||
echo "${RED}Cloning GCC repo failed!${NC}"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
./configure --prefix=/opt/riscv/gcc14-rp2350-no-zcmp \
|
||||
--with-arch=rv32ima_zicsr_zifencei_zba_zbb_zbs_zbkb_zca_zcb --with-abi=ilp32 \
|
||||
--with-multilib-generator="rv32ima_zicsr_zifencei_zba_zbb_zbs_zbkb_zca_zcb-ilp32--;rv32imac_zicsr_zifencei_zba_zbb_zbs_zbkb-ilp32--" \
|
||||
--with-gcc-src=`pwd`/gcc-14
|
||||
|
||||
if [ $RET_VALUE != 0 ]; then
|
||||
echo "${RED}Configure failed!${NC}"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
make -j$(nproc)
|
||||
|
||||
cd /home || exit
|
||||
|
||||
rm -rf /home/riscv-gnu-toolchain
|
||||
@@ -1,12 +1,8 @@
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.13)
|
||||
|
||||
include($ENV{PICO_SDK_PATH}/external/pico_sdk_import.cmake)
|
||||
|
||||
include($ENV{PICO_SDK_PATH}/pico_sdk_init.cmake)
|
||||
project(sample C CXX ASM)
|
||||
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER /usr/bin/arm-none-eabi-gcc CACHE PATH "" FORCE)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER /usr/bin/arm-none-eabi-g++ CACHE PATH "" FORCE)
|
||||
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_STANDARD 11)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
56
test_sdk.sh
Normal file → Executable file
56
test_sdk.sh
Normal file → Executable file
@@ -1,15 +1,55 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
|
||||
RED="\e[31m"
|
||||
GREEN="\e[32m"
|
||||
NC="\e[0m"
|
||||
STATUS=0
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ -z $1 ]]; then
|
||||
echo "Please provide an SDK image you want to test"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD}/test_poject,target=/home/dev $1
|
||||
docker exec pico-sdk /bin/sh -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make -j4"
|
||||
docker exec pico-sdk /bin/sh -c "picotool"
|
||||
declare -a boards=("pico" "pico_w" "pico2" "pico2_riscv" "pico2_w" "pico2_w_riscv")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source="${PWD}"/test_poject,target=/home/dev "$1"
|
||||
|
||||
for board in "${boards[@]}"
|
||||
do
|
||||
echo "---- $board build test ----"
|
||||
docker exec pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "rm -rf /home/dev/build"
|
||||
if [[ $board = pico2_riscv ]] ; then
|
||||
docker exec -i pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=pico2 -DPICO_PLATFORM=rp2350-riscv && make -j4"
|
||||
elif [[ $board = pico2_w_riscv ]] ; then
|
||||
docker exec -i pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=pico2_w -DPICO_PLATFORM=rp2350-riscv && make -j4"
|
||||
else
|
||||
docker exec -i pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=${board} && make -j4"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ $? != 0 ]; then
|
||||
echo -e "${RED}----- Test failed -----${NC}"
|
||||
STATUS=1
|
||||
break
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo "${GREEN}----- Test passed -----${NC}"
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
docker container kill pico-sdk
|
||||
docker container rm pico-sdk
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD}/freertos_test_project,target=/home/dev $1
|
||||
docker exec pico-sdk /bin/sh -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && make -j4"
|
||||
docker exec pico-sdk /bin/sh -c "picotool"
|
||||
docker container kill pico-sdk
|
||||
docker container rm pico-sdk
|
||||
exit ${STATUS}
|
||||
|
||||
# for board in "${boards[@]}"
|
||||
# do
|
||||
# echo "FreeRTOS $board build test"
|
||||
# docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD}/freertos_test_project,target=/home/dev $1
|
||||
# if [[ $board -eq "pico2_riscv" ]] ; then
|
||||
# docker exec pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=pico2 -DPICO_PLATFORM=rp2350-riscv && make -j4"
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# docker exec pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "cd /home/dev && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DPICO_BOARD=${board} && make -j4 && cd .. && rm -rf build"
|
||||
# fi
|
||||
# docker exec pico-sdk /bin/bash -c "rm -rf /home/dev/build"
|
||||
# docker container kill pico-sdk
|
||||
# docker container rm pico-sdk
|
||||
# rm -rf ./test_poject/build/
|
||||
# done
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user