forked from andrey/raspberry-pi-pico-docker-sdk
142 lines
5.9 KiB
Markdown
142 lines
5.9 KiB
Markdown
[](https://github.com/lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-docker-sdk/actions/workflows/sdk-ci.yml)
|
|
|
|
# Raspberry Pi Pico Docker SDK
|
|
|
|
Lightweight Raspberry Pi Pico C++ SDK container.
|
|
|
|
## Pull container from Docker Hub and run
|
|
|
|
The latest version of the image is stored on [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk/general)
|
|
and can be used for container runs.
|
|
Commands below show how to run a container, using an image from Docker Hub
|
|
```
|
|
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk:latest
|
|
|
|
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The directory from which the `docker run` command was called will be mounted to /home/dev in the container.
|
|
So after attaching to the SDK container you can build your project following the steps:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
cd /home/dev
|
|
|
|
mkdir build
|
|
|
|
cd build
|
|
|
|
cmake .. && make -j4
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Build image and run container:
|
|
|
|
To build your own SDK image, You need to clone this repository and run the following commands:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
cd raspberry-pi-pico-docker-sdk
|
|
|
|
docker build . --tag pico-sdk
|
|
|
|
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev pico-sdk
|
|
|
|
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Visual Studio Code as Rassberry Pi PICO projects IDE
|
|
|
|
You can use the SDK container with Visual Studio Code as Raspberry Pi Pico projects IDE.
|
|
|
|
### Attaching VSCode to SDK Docker container
|
|
|
|
Follow the instruction below to set up VSCode:
|
|
|
|
1. Install [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) and next [Remote Development](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode-remote.vscode-remote-extensionpack) extensions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Open the terminal and go to the projects you want to open in VSCode.
|
|
|
|
3. Pull SDK image from Docker HUB and run SDK container via the following command. The container must be running while you attach to it via VSCode.
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
docker run -d -it --name pico-sdk --mount type=bind,source=${PWD},target=/home/dev lukstep/raspberry-pi-pico-sdk:latest
|
|
|
|
docker exec -it pico-sdk /bin/sh
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
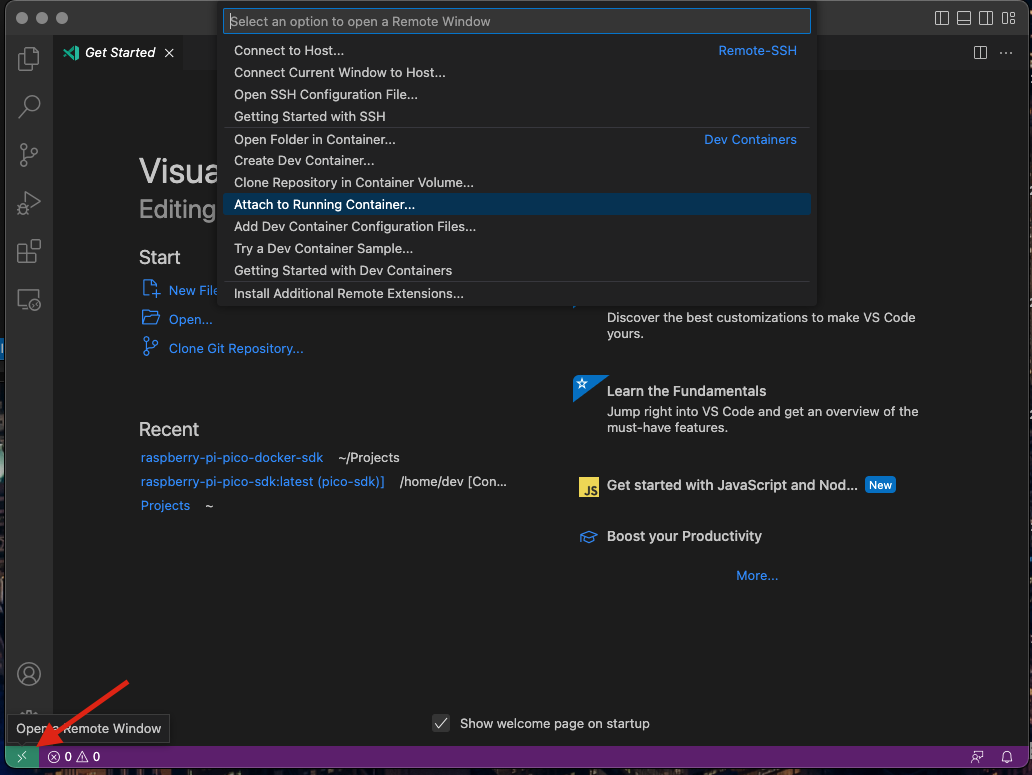
4. When the container is launched, go to VSCode, click the green button in the lower left corner of VSCode and select options: Attach to Running Container...
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
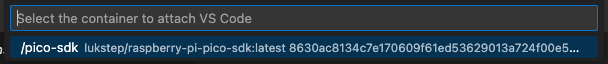
5. Select the SDK container.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. Then a new VSCode window will open. At the bottom window, you can see that it is attached to the SDK container.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
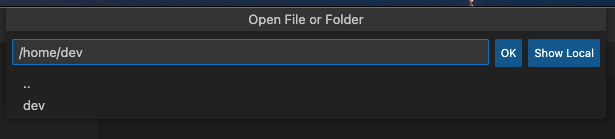
7. Now, there is needed to open project files. Your project is mounted to `/home/dev` in the container. Go to EXPLORE tab in VSCode and click Open Folder. In opened window write `/home/dev` and click the OK button.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. Now You can explore, develop and build your Raspberry Pi Pico project via Visual Studio Code!
|
|
|
|
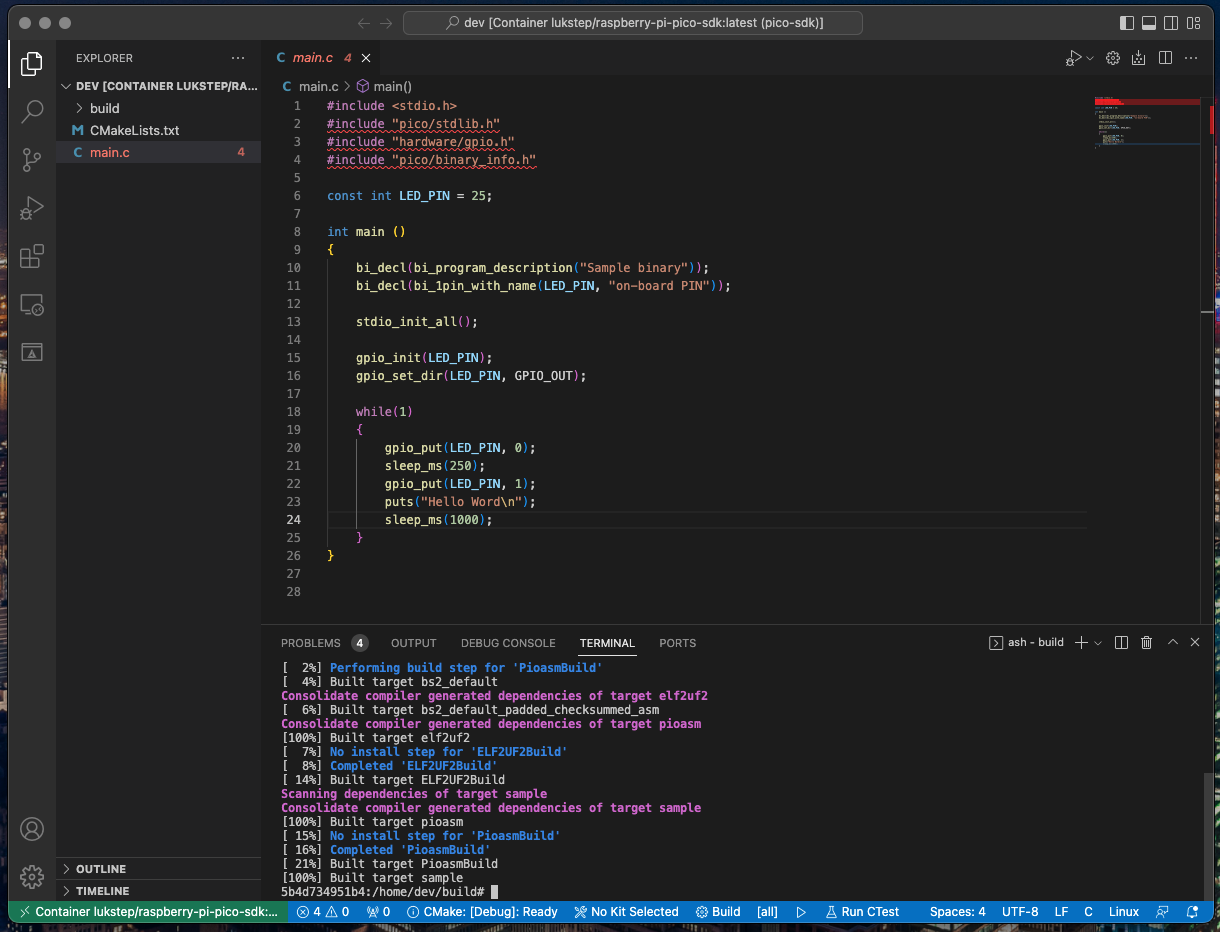
|
|
|
|
### Pico SDK aware Intellisense
|
|
|
|
For an IntelliSense that will be aware of Raspberry Pi Pico SDK dependencies, we will use [Clangd](https://clangd.llvm.org). Clangd is a C/C++ language server provided by the LLVM project. To Setup Clang as Intellisense engine follow instruction below:
|
|
|
|
1. To begin with, you need to install the server itself (Clangd is not installed by default in the SDK container image), to do this in the terminal call the command:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
apk add clang-extra-tools
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
2. Next is needed to install the Visual Studio Code [Clangd extension](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=llvm-vs-code-extensions.vscode-clangd).
|
|
|
|
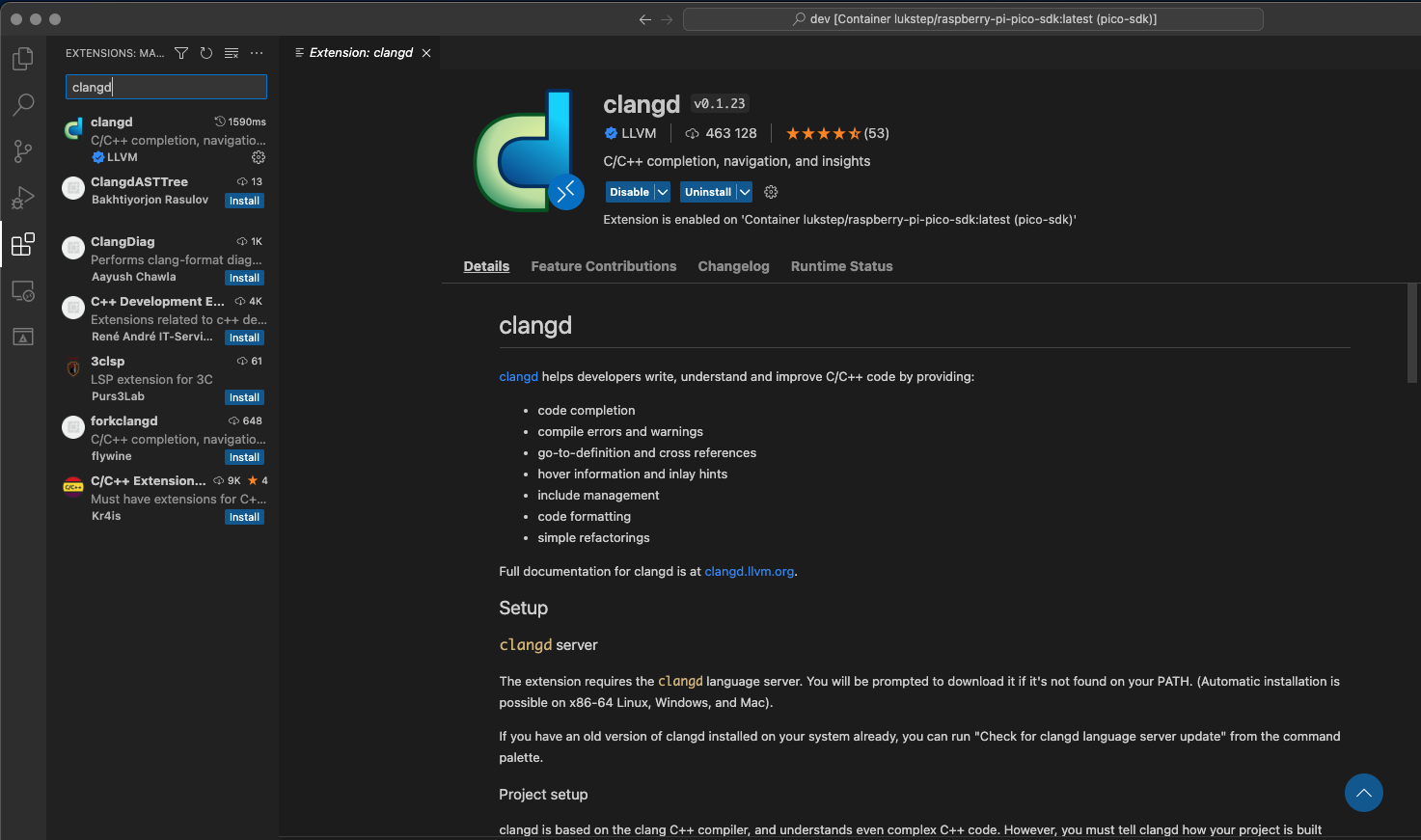
|
|
|
|
1. To set-up The Clangd extension, in the project root directory, create folder .vcode with file settings.json. To settings.json past configuration from the snippet below:
|
|
|
|
```json
|
|
{
|
|
"C_Cpp.intelliSenseEngine": "Disabled",
|
|
"clangd.path": "/usr/bin/clangd",
|
|
"clangd.checkUpdates": false,
|
|
"clangd.restartAfterCrash": true,
|
|
"clangd.detectExtensionConflicts": true,
|
|
"clangd.arguments": ["-log=verbose",
|
|
"-pretty",
|
|
"--background-index",
|
|
"--query-driver=/usr/bin/arm-none-eabi-gcc",
|
|
"--compile-commands-dir=/home/dev/build"]
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
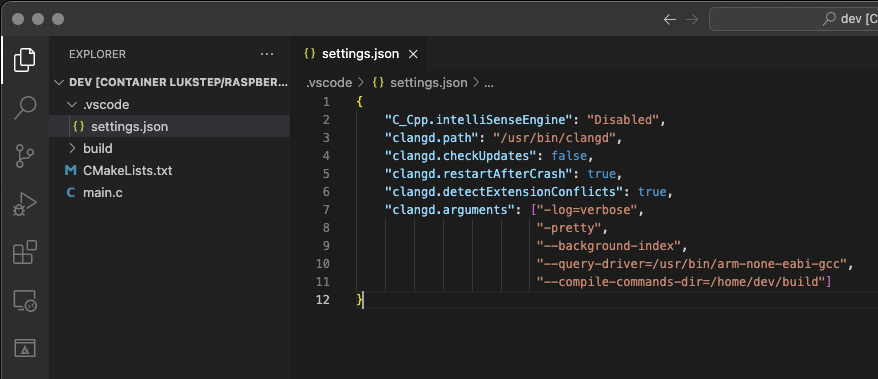
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. For clangd to work, it needs a `compile_commands.json` file. This file contains the compilation and dependency information of each file in the project. To create it you need to add to the CMake command, `-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1`. So You need to build your project with the command:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
mkdir build
|
|
|
|
cd build
|
|
|
|
cmake -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=1 ..
|
|
|
|
make
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
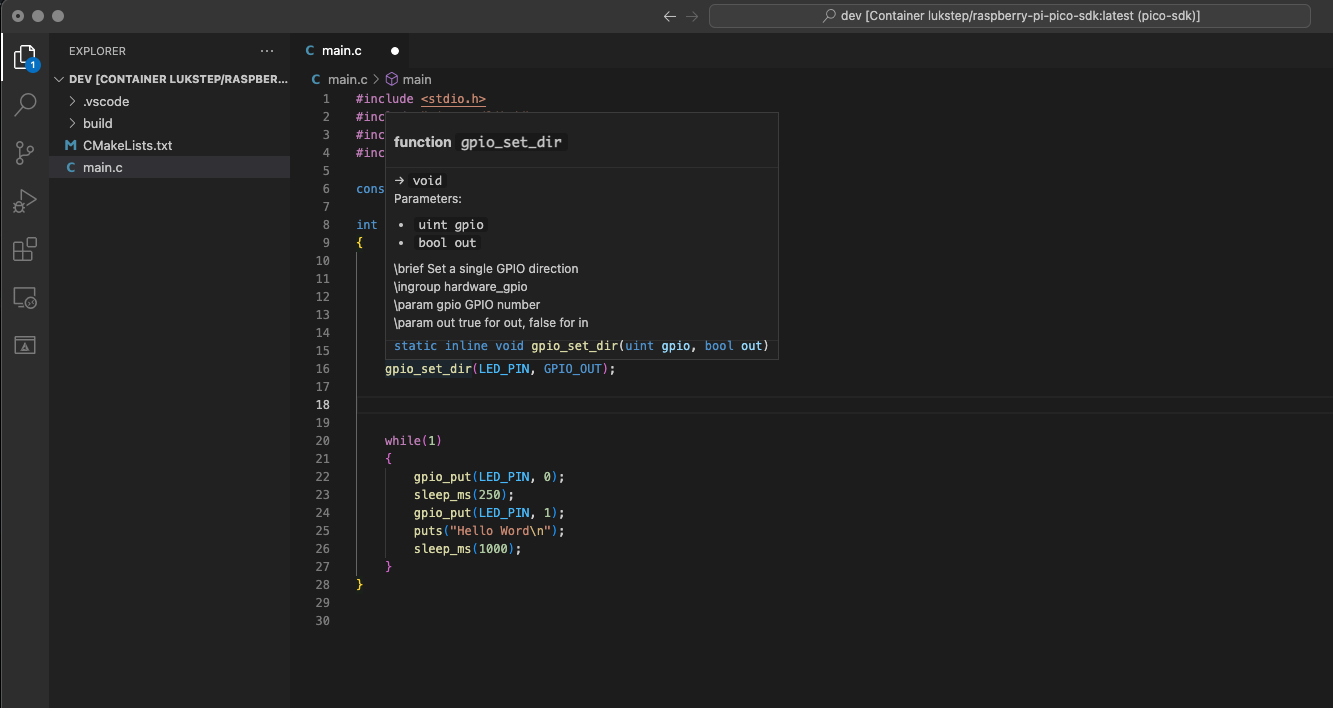
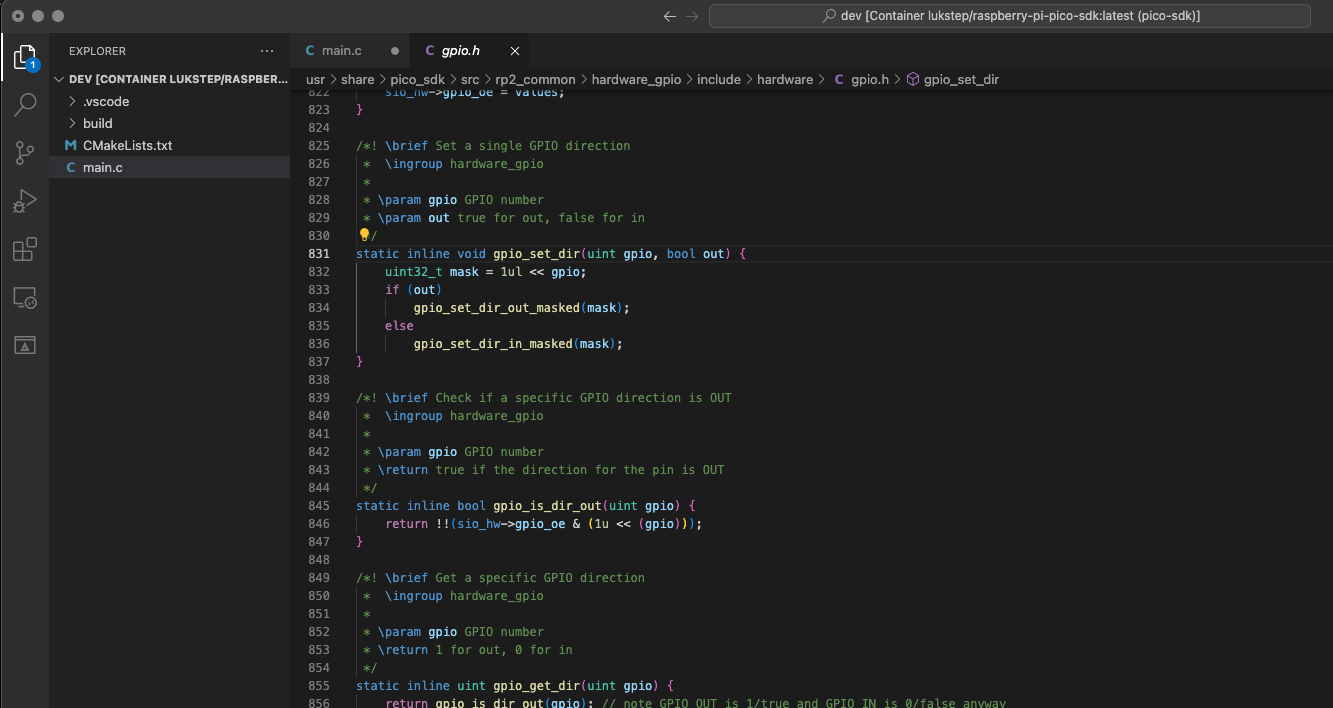
5. Now IntelliSense should work!. Now you should see a prompt when you start typing. If you hover your cursor over a function from the SDK you should see its documentation, You can go to the function definition by pressing F12.
|
|
|
|
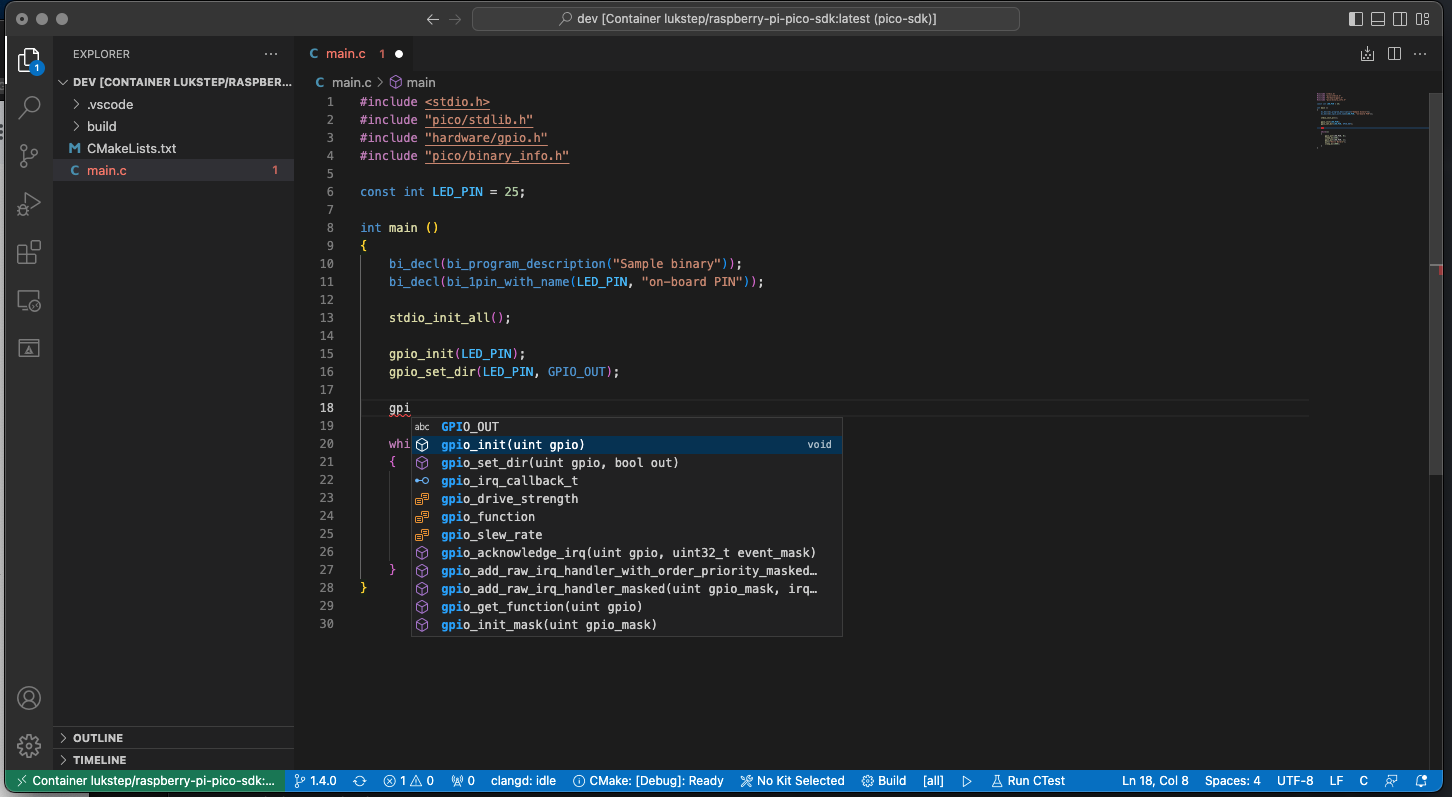
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|